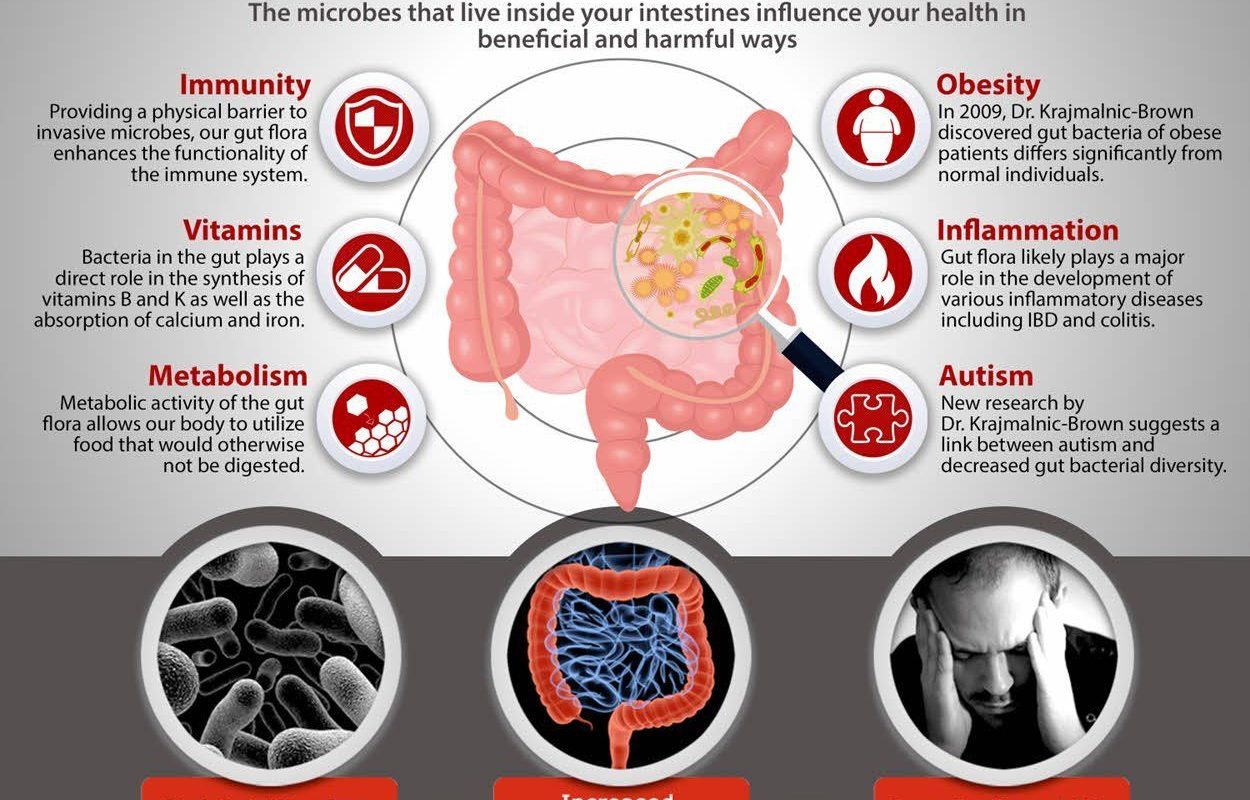
Gut microbiota, also known as gut flora or gut bacteria, refers to the trillions of microorganisms residing in our gastrointestinal tract. Over the past decade, research on gut microbiota has rapidly expanded, shedding light on its crucial role in human health and well-being. This article explores the latest findings on gut microbiota and discusses its impact on various aspects of human health.
The Complex World of Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota constitutes a complex ecosystem consisting of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. It plays a vital role in maintaining the balance and functioning of our digestive system and performing several important functions.
Diversity and Composition
Research has revealed that the gut microbiota varies significantly among individuals, influenced by factors such as genetics, diet, geographic location, and lifestyle choices. The variation in gut microbiota composition can impact an individual’s susceptibility to certain diseases and overall health.
Metabolic Activities
Gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in various metabolic activities, including the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, production of essential vitamins, and influencing the metabolism of certain drugs. Recent studies have linked alterations in gut microbiota to metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Gut Microbiota and Immune System
The gut microbiota has a profound influence on the development and regulation of the immune system. It helps train the immune system to recognize and respond appropriately to pathogens while maintaining tolerance towards harmless substances. Dysregulation of gut microbiota has been associated with autoimmune diseases, allergies, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Impact on Mental Health
Emerging evidence suggests a strong connection between gut microbiota and mental health. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain, influences processes such as stress response, mood regulation, and neurotransmitter production. Alterations in gut microbiota composition have been linked to mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression.
Strategies to Promote a Healthy Gut Microbiota
With the growing understanding of the importance of gut microbiota, there is increasing interest in strategies to promote a healthy balance. Some approaches include:
Dietary Modifications
A well-balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. On the other hand, excessive consumption of processed foods, high sugar intake, and low-fiber diets can negatively impact gut microbiota diversity.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed, while prebiotics are substances that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and fermented products, as well as prebiotic-rich foods such as onions, garlic, and bananas, can support a healthy gut microbiota.
Avoidance of Unnecessary Antibiotics
While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, their overuse can disturb the delicate balance of gut microbiota. It is important to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary, as their indiscriminate use can lead to long-term disruptions in gut health.
Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in human health and has far-reaching effects on various aspects of our well-being. Understanding the latest findings on gut microbiota reinforces the importance of maintaining a healthy and diverse gut ecosystem through lifestyle choices, diet, and judicious use of antibiotics. Further research in this field holds great promise for developing personalized interventions to improve health outcomes and manage various gut-related disorders.