Our gut and brain are intrinsically connected, and this relationship plays a fundamental role in our mental health. Recent scientific research has shed light on the significance of the gut-brain connection, highlighting how our nutritional choices impact our mental well-being.
The Gut Microbiota
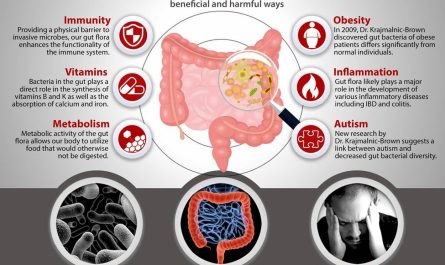
The gut microbiota refers to the complex community of microorganisms that inhabit our digestive system, primarily in our intestines. It exerts a powerful influence on our overall health, including mental health. The gut microbiota plays a vital role in various physiological processes, such as digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system regulation.
The Brain-Gut Axis
The brain-gut axis is a bidirectional communication system between our central nervous system and the enteric nervous system of our gastrointestinal tract. This communication occurs through neural, hormonal, and immune pathways. The brain can influence digestive function, while the gut microbiota can influence our brain and mental health.
Impact on Mental Health
Emerging evidence suggests that the gut microbiota has a profound impact on mental health. Imbalances in the gut microbiota, referred to as dysbiosis, have been linked to various mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Inflammation and Mood
Inflammation in the body, often associated with an unhealthy diet, can contribute to the development of mental health disorders. The gut microbiota regulates our immune system and plays a role in determining the level of systemic inflammation. Chronic inflammation can lead to mood disturbances and increased susceptibility to mental illness.
The Role of Diet
Mounting evidence suggests that a healthy diet is crucial for maintaining a balanced gut microbiota and supporting mental well-being. A diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and fermented products promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, added sugars, and saturated fats can disrupt the gut microbiota and promote inflammation, negatively impacting mental health.
Probiotics and Mental Health
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that provide numerous health benefits, particularly for the gut microbiota. Research suggests that certain strains of probiotics can positively impact mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress. Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can be beneficial additions to a balanced diet.
Prebiotics and Mental Health
Prebiotics are indigestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial bacteria in the gut. By promoting the growth of these bacteria, prebiotics can have a positive impact on mental health. Foods rich in prebiotics include whole grains, onions, garlic, bananas, and legumes. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help support a healthy gut microbiota and improve mental well-being.
The Impact of Stress
Stress is a significant factor that can disrupt the gut-brain connection. Chronic stress alters the composition of the gut microbiota and weakens the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to increased susceptibility to mental health disorders. Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can help protect the gut-brain connection.
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating field of research that highlights the importance of a balanced diet and a healthy gut microbiota for maintaining optimal mental health. By prioritizing nutrition, managing stress, and incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into our diets, we can nurture the gut-brain connection and support our mental well-being.