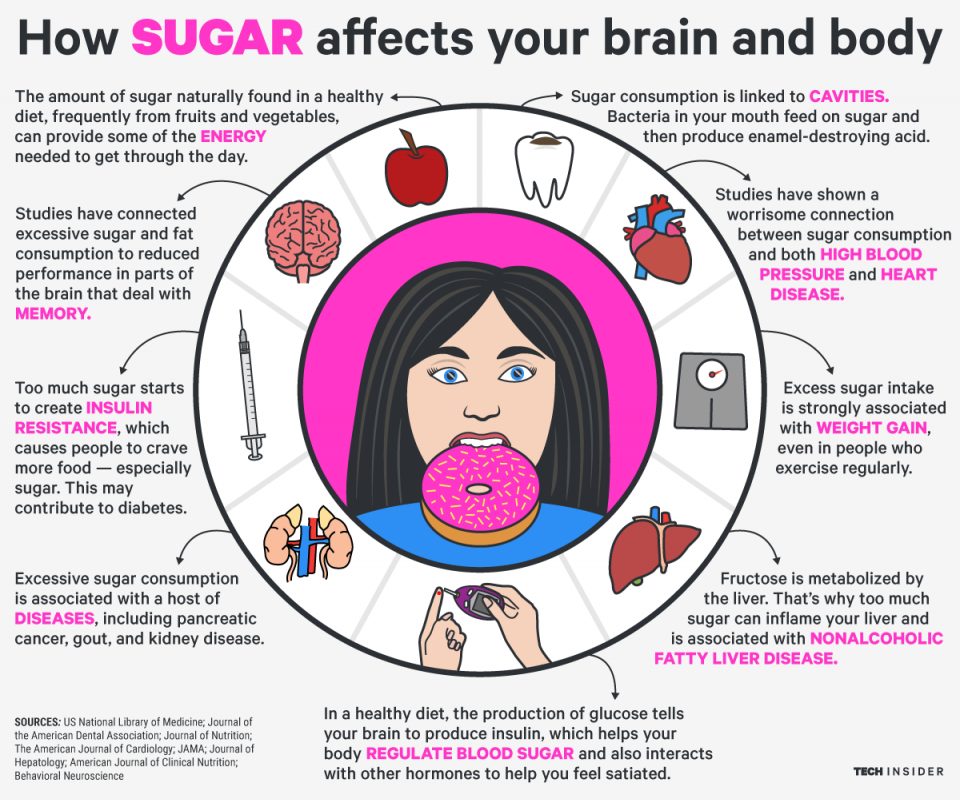
Sugar consumption has always been a controversial topic when it comes to its impact on health. While sugar undoubtedly adds a delightful taste to our lives, excessive consumption has been linked to various health problems. In this article, we will explore the scientific perspectives on how sugar affects our health.
The Role of Sugar in Our Diet
Sugar, in its various forms like sucrose and high fructose corn syrup, is a common ingredient found in many processed foods and beverages. It provides a quick burst of energy, making it popular for immediate fueling. However, it also delivers empty calories as it lacks essential nutrients.
The Sugar and Chronic Diseases Connection
Scientific studies have unveiled a strong association between excessive sugar intake and the development of chronic diseases. High sugar diets have been linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, and even certain types of cancers. The consumption of sugary beverages, especially, has been linked to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity-related diseases.
The Blood Sugar Rollercoaster
When we consume sugary foods, our blood sugar levels rapidly spike. This triggers the release of insulin to regulate blood sugar. However, this hormonal response often leads to a subsequent crash in blood sugar levels, causing energy dips and cravings for more sugary foods. This rollercoaster effect can disrupt our energy levels and overall well-being.
Sugar and Dental Health
Sugar consumption also poses a significant threat to our dental health. Bacteria in our mouths feed on sugar, producing acids that erode tooth enamel and lead to cavities. Regularly consuming sugary snacks or drinks can contribute to tooth decay and other dental issues, especially if proper oral hygiene practices are not followed.
Sugar and Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a potential link between excessive sugar intake and mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. While the precise mechanisms are not fully understood, studies have found that a high-sugar diet may increase inflammation in the brain and interfere with the production and functioning of neurotransmitters.
Hidden Sources of Sugar
One of the biggest challenges in reducing sugar intake is identifying hidden sources of sugar in our diets. Many processed foods and beverages, including seemingly healthy options, contain added sugars that may not be immediately apparent. Reading food labels and being mindful of ingredient lists can help in making more informed choices about sugar consumption.
Recommended Sugar Intake
Scientific organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Heart Association (AHA) have issued guidelines for recommended sugar intake. Both suggest limiting the consumption of added sugars to no more than 10% of daily calorie intake. For an average adult, this corresponds to approximately 50 grams or 12 teaspoons of added sugar per day.
Moderation is Key
While it is important to be mindful of sugar intake, complete elimination is neither practical nor necessary for most individuals. Enjoying sugary treats in moderation can still be a part of a healthy diet. The key lies in striking a balance, making conscious choices, and focusing on a varied and nutrient-rich eating pattern.
Scientific perspectives suggest that excessive sugar consumption can have detrimental effects on our health, contributing to various chronic diseases and dental problems. Being aware of hidden sources of sugar and adhering to recommended intake guidelines are crucial steps towards maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By striking a balance and practicing moderation, we can still satisfy our sweet tooth without compromising our long-term well-being.